UAE is a dynamic region, constantly adapting and changing legal and employment rules.
The UAE Labor Law has been updated for 2024 to incorporate changes that benefit both employers and employees alike.
UAE Labor Law 2026 has also been updated, with modifications designed to safeguard workers’ rights and conform to modern employment standards.
Understanding labor laws is crucial to creating long-lasting relationships between employers and employees, meeting legal compliance obligations and creating an equitable work environment.
This guide details the latest updates made to UAE Labor Law 2026.
Table of contents
Recent Updates in UAE Labor Law 2026
The UAE Labor Law of 2026 places greater emphasis on flexible work options, employee rights and employer responsibilities.
Here are the key updates:
Work Models:
The 2026 labor law introduced various work arrangements, such as:
-
- Full-time: Regular work with fixed weekly hours.
-
- Part-time: work offers flexible hours with reduced commitment requirements than full-time employment does.
-
- Temporary: We offer short-term contracts designed for specific projects or time frames.
-
- Freelance: Independent work without a long-term commitment to one employer.
Leave Policy:
Although there are no significant changes to leave policies, the law continues to emphasize the importance of paid leave, including:
-
- Annual leave
-
- Maternity leave
-
- Sick leave
End-of-Service Benefits:
End-of-service benefits remain a key part of the labor law, especially for expatriates.
Employers must calculate and pay gratuities and other benefits according to the updated legal requirements.
Employment Contracts in UAE Labor Law 2026

Employment contracts are legally binding agreements that define the relationship between employers and employees.
They typically include details such as:
-
- Date of joining
-
- Job title
-
- Salary
-
- Duration of employment
-
- Termination and notice period
The 2026 labor law outlines the following types of contracts, each with its own rules:
1. Full-Time Contracts:
-
- Employees work 40–48 hours weekly.
-
- Contracts must define fixed terms, including salary, benefits, and notice periods (30–90 days).
2. Part-Time Contracts:
-
- Part-time employees work fewer hours with flexible schedules.
-
- They are entitled to proportional benefits, such as wages, leave, and end-of-service gratuities.
3. Temporary Contracts:
-
- Suitable for seasonal or short-term projects.
-
- Employers must define the project duration and early termination terms.
-
- Employees receive agreed-upon benefits and a notice period.
4. Freelance Contracts:
-
- Freelancers work independently and are not bound by one employer.
-
- While they do not receive standard employee benefits, contracts must ensure fair payment and comply with UAE labor law.
This comprehensive update to the UAE labor law aims to create a fair and balanced workplace, adapting to modern employment practices.
Types of Leave in UAE Labor Law
The UAE Labor Law provides various types of leave to promote employee well-being and balance between personal and professional life.

Here’s a simplified overview:
1. Annual Leave:
-
- Employees are entitled to 30 calendar days of paid leave after completing one year of work.
-
- This helps maintain a healthy work-life balance, boosts satisfaction, and improves productivity.
-
- Unused leave can be carried over in certain cases.
2. Sick Leave:
-
- Employees can take up to 90 days of sick leave per year, divided as follows:
-
- First 15 days: Full pay
-
- Next 30 days: Half pay
-
- Last 45 days: Unpaid
-
- This ensures employees recover properly, prevents illness from spreading, and maintains trust and morale within the organization.
3. Maternity Leave:
-
- Female employees are entitled to 60 days of maternity leave:
-
- First 45 days: Full pay
-
- Last 15 days: Half pay
-
- This allows mothers to recover after childbirth and bond with their babies. The law also supports gender equality in the workplace.
4. Paternity Leave:
-
- Male employees can take five days of paid leave within one month of their child’s birth.
-
- This encourages fathers to participate in early childcare and enhances family support and work-life balance.
5. Compassionate Leave:
-
- Employees may take leave for personal emergencies based on the employer’s discretion.
-
- For bereavement:
-
- Death of a spouse: 5 days of paid leave
-
- Death of a parent, child, sibling, grandchild, or grandparent: 3 days of paid leave
6. Hajj Leave:
-
- Employees can request up to 30 days of unpaid leave to perform Hajj.
-
- This leave is only available once during their entire period of employment with the company.
7. Umrah Leave:
-
- The law does not specifically grant leave for Umrah.
-
- Employers may allow employees to take annual leave or unpaid leave for Umrah, based on their discretion.
This range of leave options supports employees’ personal needs while fostering a positive and balanced work environment.
Wages in UAE Labor Law
In the UAE, wages (the salary or pay that an employee receives) depend on many factors including type of work performed, industry in which it occurs and nationality of employee.
Wage Protection System (WPS) is used to pay salaries. This system ensures that employees’ pay checks reach their bank accounts or authorized financial institutions as soon as possible.
The Ministry of Human Resources and Emiratisation (MOHRE) does not handle the salary transactions directly.
Here are the ways salaries are paid:
-
- In Emirati Dirhams (AED): Emirati Dirhams (AED) are the official currency of the UAE.
-
- In another currency: If both the employer and employee agree in the contract, the salary can be paid in another currency.
Current UAE legislation does not set an official minimum wage; however, employees should earn enough to meet their basic needs.
Working Hours as per UAE Labor Law:
-
- Normal working hours: Employees usually work 8 hours a day, which adds up to 48 hours a week.
-
- During Ramadan: Muslim employees work six-hour days instead of eight, as it’s an important period for fasting.
-
- This law also permits remote work, flexible hours and part-time employment to provide workers with more options in their work schedules.
Overtime in UAE Labor Law:
If an employee works more hours than required, they are entitled to overtime pay. Here’s how overtime compensation is calculated:
-
- Overtime during regular hours: Employees working additional hours will receive 25% more in their salary due to any overtime hours worked.
-
- Night shift: Employees working between 10 PM and 4 AM are entitled to receive 50% extra in addition to their regular salary.
-
- Working on rest days or public holidays: Employees working on rest days or public holidays receive 50% extra pay, plus either time off or an additional day of rest.
Rest Days and Public Holidays

-
- Employees are entitled to one paid rest day per week, which is usually Friday, but it can be any day depending on the employment contract.
-
- Public holidays: Employees in both private and public sectors must get a day off on public holidays. These holidays include:
-
- Gregorian New Year (1 January)
-
- Eid Al Fitr (4 days)
-
- Arafat Day and Eid Al Adha (4 days)
-
- Hijra New Year (Islamic New Year)
-
- Prophet Mohammed’s Birthday
-
- National Day (2 days)
Termination of Employment:
When an employee’s contract ends, it can happen in several ways, as per UAE Labor Law:
-
- Notice period: Employees or employers can end the contract after giving a 30-day notice, but the notice period can be between 30 and 90 days, depending on the contract.
-
- Immediate termination: If the employee commits serious misconduct (like breaking company rules), they can be fired immediately without any prior notice.
Reasons for Termination:
Here are some common reasons an employer might terminate an employee:
-
- Underperformance: If the employee is not performing well at work.
-
- Misconduct: For example, if an employee shares confidential company information or engages in violence at work.
-
- Policy violations: Repeatedly breaking company rules despite warnings.
-
- Redundancy: If the company needs to restructure or cut costs, certain positions may be eliminated.
-
- Arbitrary dismissal: This is an illegal termination without valid reasons. Employees who are unfairly fired can file a complaint with MOHRE or the labor court.
Gratuity (End-of-Service Benefit):
-
- Gratuity is a bonus that employees get when they leave a job after working for at least one year.
-
- The gratuity amount is calculated based on the employee’s basic salary and length of service.
-
- Employees can use a UAE Gratuity Calculator to calculate their end-of-service benefits easily.
Health and Safety Regulations:
UAE Labor Law includes strict health and safety regulations to protect employees:
-
- Safe working environment: Employers must ensure that the workplace is safe and free from hazards.
-
- Risk assessment: Regular checks must be done to identify and eliminate potential risks at work.
-
- Emergency preparedness: Employers must have emergency plans in place, such as fire drills and accessible fire escapes.
-
- Health and safety training: Employees must receive training on how to stay safe at work.
-
- Medical care: Employers must provide medical care to employees, especially in high-risk industries like construction and manufacturing.
-
- Rest breaks: Employees should get enough breaks to avoid exhaustion.
-
- Accommodation: Employers who provide housing must ensure that living conditions are safe, clean, and comfortable.
Health Insurance:
Employers must provide health insurance for their employees, covering hospital stays and medical expenses.
The cost of the health insurance must be paid by the employer, not the employee.
Disputes
If a dispute arises between an employee and employer, it can be resolved through the following steps:
-
- Filing a complaint with MOHRE: Employees or employers can file a complaint online or at a service center.
-
- Mediation: MOHRE will try to help both sides reach an agreement.
-
- Labor court: If mediation doesn’t work, the case goes to court, where evidence is presented, and a decision is made.
Work Permits and Visas
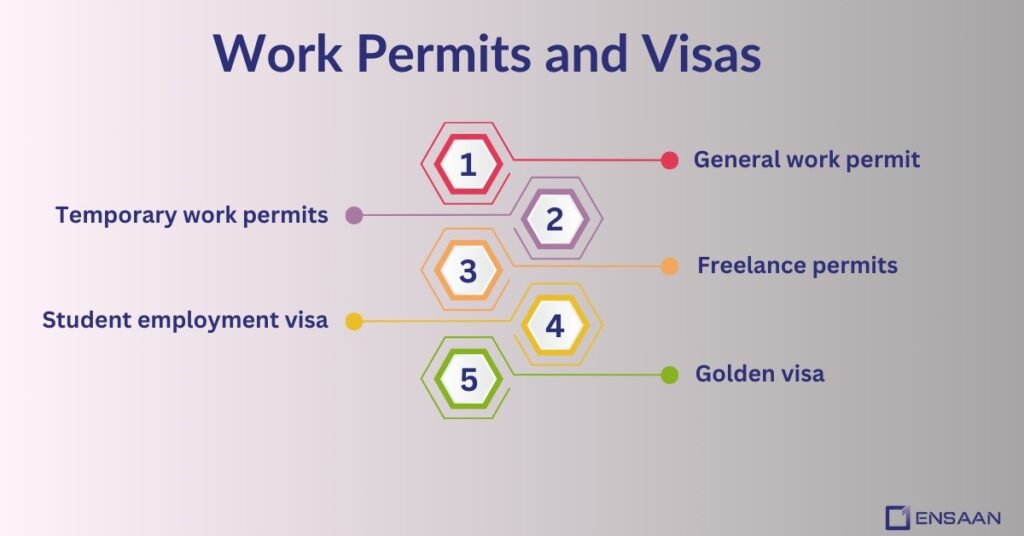
To work in the UAE, you need a work permit. There are several types of work permits, including:
-
- General work permit: For hiring foreign employees.
-
- Temporary work permits: For specific, short-term projects.
-
- Freelance permits: For self-employed people working on their own.
-
- Student employment visa: For students working part-time.
-
- Golden visa: For long-term residents or investors.
Emiratisation
The UAE government has a program called Emiratisation to encourage hiring more UAE nationals.
By 2026, the government aims to have 10% of private sector jobs filled by Emiratis. The NAFIS program trains young Emiratis to help them find jobs in the private sector.
Types of Companies You Can Setup in the UAE

When starting a business in the UAE, it’s important to choose the right company structure.
Each type has its own rules, advantages, and limitations, so it’s crucial to understand your options before planning.
1. Limited Liability Company (LLC):
An LLC is one of the most common business types in the UAE. It allows both local and foreign ownership, with at least two shareholders and a maximum of 50.
-
- Key Benefits: The main advantage of an LLC is that shareholders’ personal assets are protected from business debts. It also offers flexibility in how the business is managed and can be involved in many different types of activities.
-
- Key Drawbacks: To form an LLC, you need a local sponsor (a UAE national) to own at least 51% of the shares. However, foreign investors can still control the business operations fully.
2. Free Zone Company:
Free zone companies are set up in special areas in the UAE where businesses can enjoy certain benefits, like 100% foreign ownership and tax exemptions.
There are over 45 free zones, each catering to different industries.
-
- Key Benefits: You get full foreign ownership and don’t have to pay import/export taxes. These zones make it easier for businesses to trade internationally.
-
- Key Drawbacks: Free zone companies can only do business within the free zone or internationally. They can’t conduct business directly in the UAE mainland.
3. Branch Office:
A branch office allows a foreign company to operate in the UAE without creating a new company. It is an extension of the parent company.
-
- Key Benefits: There’s no need for share capital, and the parent company has full control. The branch can carry out the same business activities as the parent company.
-
- Key Drawbacks: A local agent (a UAE national) must be hired to act as a service agent. The branch is also not fully independent from the parent company, which means its decisions and operations are tied to the parent.
4. Representative Office:
A representative office is set up by foreign companies to promote and market their products or services within the UAE market, without creating revenue or sales itself.
-
- Key Benefits: There’s no need for share capital and it provides companies with an effective means of breaking into the UAE market.
-
- Key Drawbacks: An office cannot directly engage in sales activities that generate income; rather, its primary function is marketing and promotion – making it less suitable for businesses looking to sell directly in UAE markets.
Conclusion
UAE Labor Law 2026 introduces changes that aim to create a fair, safe, and efficient work environment.
Employers and employees must stay informed and comply with the law to ensure mutual benefits and contribute to the growth of the UAE economy.
FAQ
1. What is the UAE Labor Law 2026?
It’s the set of rules that protect employees’ rights and define employer responsibilities in the UAE.
2. What are the different types of work models under the 2026 law?
The law recognizes full-time, part-time, temporary, and freelance work models.
3. How much annual leave are employees entitled to?
Employees get 30 days of paid leave per year after completing one year of work.
4. How is sick leave managed?
Employees can take up to 90 days of sick leave. The first 15 days are with full pay, the next 30 days with half pay, and the last 45 days are unpaid.
5. What is maternity leave like?
Women get 60 days of maternity leave, with the first 45 days paid in full and the last 15 days at half pay.